JavaScript Engine
The JavaScript engine is a program that executes your JavaScript code. A popular example of a JavaScript engine is Google’s V8 engine.
V8 Engine
The V8 engine is an open-source, high-performance JavaScript and Web Assembly engine written in C++. The V8 engine is used inside Google Chrome, Node.js, and electron, among others. The V8 engine has two main components
- Heap is an unstructured memory that is used for memory allocation of the variables and the objects.
- Call Stack is a LIFO data structure that is used for function calls that record where we are in the program.
Call Stack
JavaScript is a single-threaded programming language, which means it can do one thing at a time, and it has one Call Stack.
If you call a function, it’s pushed on the top of the Call Stack, and when the function returns, it’s popped from the top of the Call Stack.
Let’s take an example.
Call Stack Visualization

Let’s take another example that contains an error.
Call Stack Visualization

When the V8 engine encounters an error, it prints a stack trace. A stack trace is basically the state of the Call Stack.
Let’s take another example that blows up the Call Stack
We can do this by using a recursive function.
Call Stack Visualization

A recursive function calls itself again and again. At some point in time, the number of function calls exceeds the actual size of the stack, and the browser detects this to take action by throwing an error.
I hope now you have a fair understanding of how JavaScript works.
Web APIs
The Web APIs are provided by the web browser that gives additional functionality to the V8 engine.
The Web API calls are added to the Web API Container from the Call Stack. These Web API calls remain inside the Web API Container until an action is triggered. The action could be a click event or HTTP request, or a timer finishes its set time. Once an action is triggered, a callback function is added to the Callback Queue.
Callback Queue
The Callback Queue is a FIFO data structure.
The Callback Queue stores all the callback functions in the order in which they are added.
Event Loop
What happens when you have function calls that take a large amount of time to execute in the Call Stack?
For example
- Executing a for loop from 1 to 10B
- Making a network request
- Doing image processing
Let’s take an example.
Synchronous Code Visualization
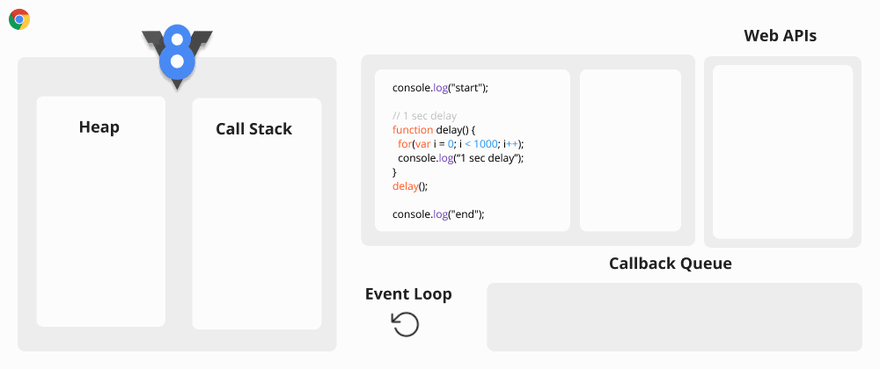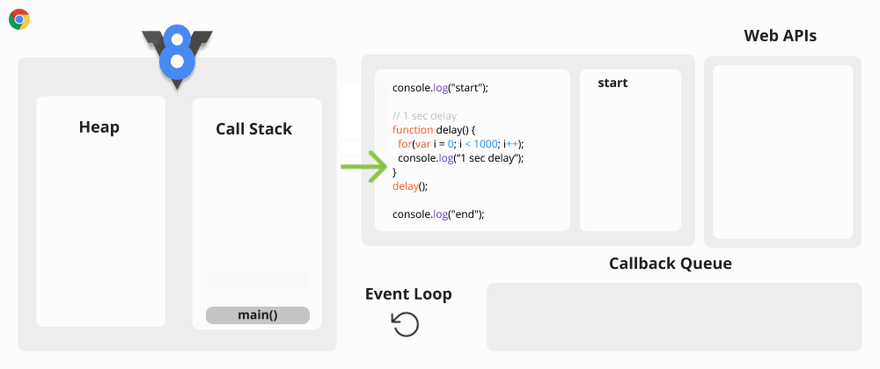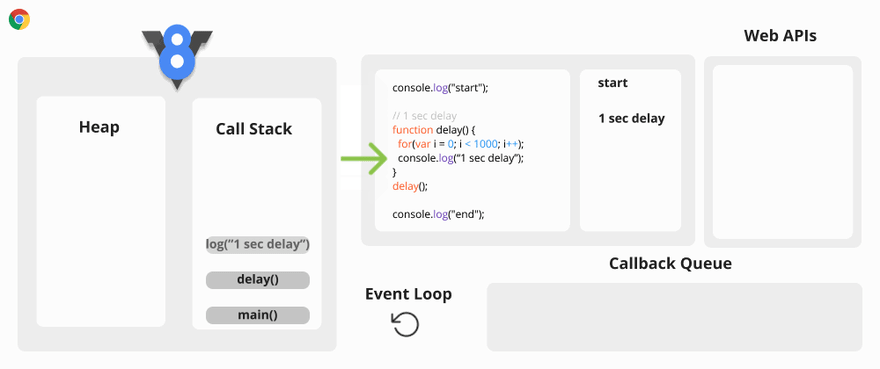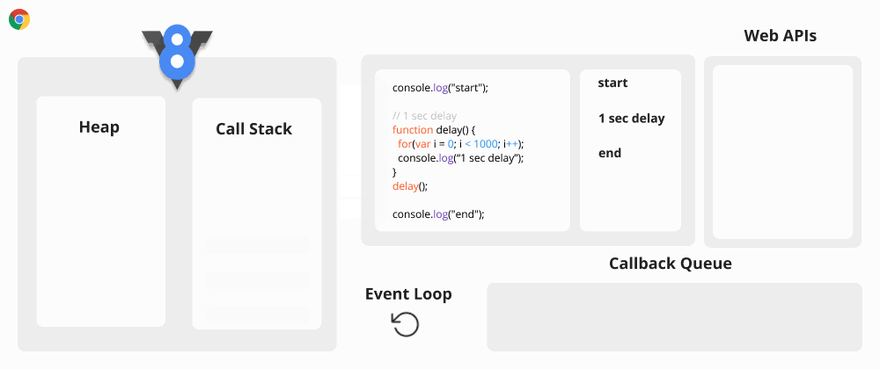
You may ask why this is a problem? The problem is when the Call Stack has a function to execute, the browser cannot do anything else because it is blocked.

The solution is an asynchronous callback, promises, and async / await.
Let’s take an example.
Asynchronous Code Visualization
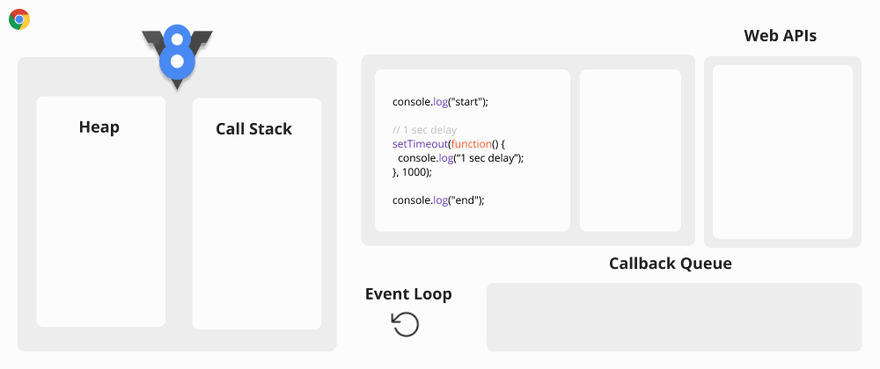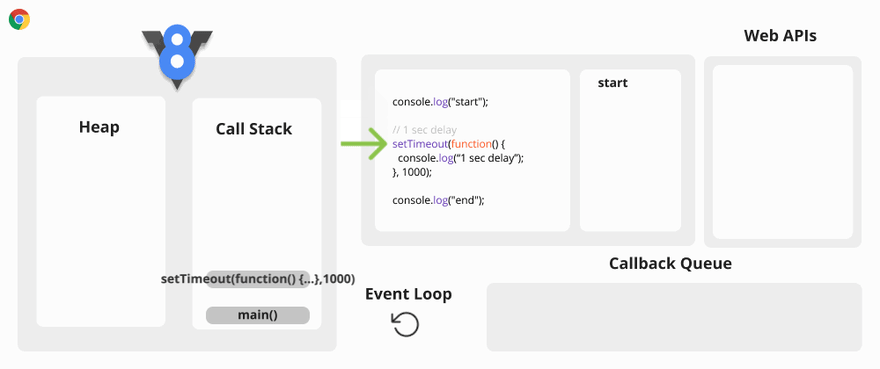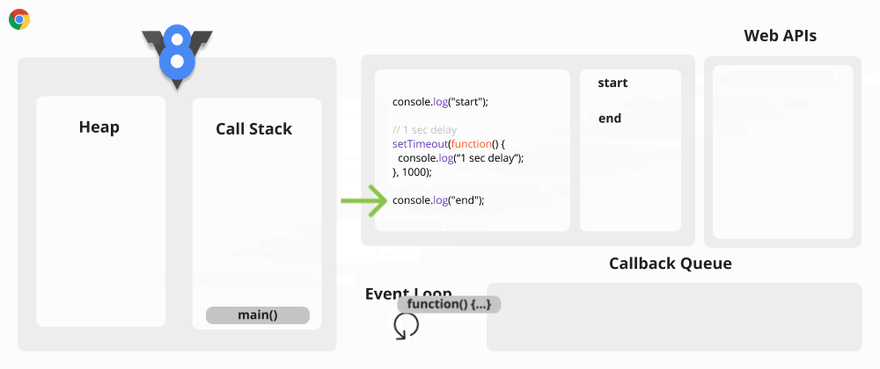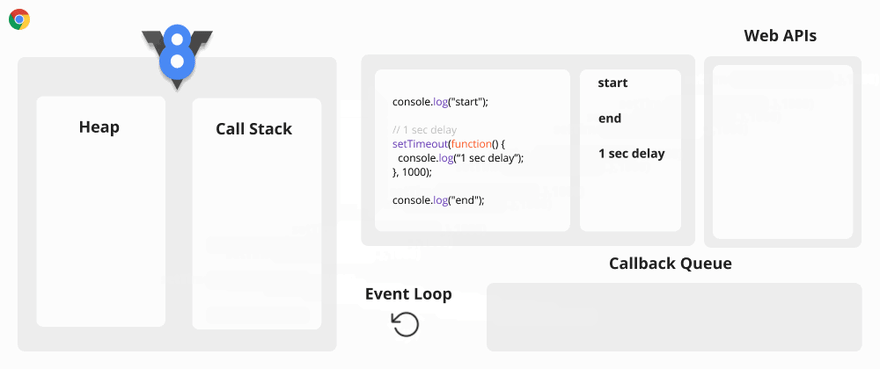
The Event Loop has only one simple job to do. It looks at the Call Stack and Callback Queue, if the Call Stack is empty, it pushes the first callback function of the Callback Queue to the Call Stack..